

The activity and sensitivity of muscle spindles can be altered by exercise training. (1) by stretch of the whole muscle, and (2) by stimu-lation of the gamma motor neurons that produce con-traction of the ends of the muscle spindle. Note that the muscle spindle can be stretched by two mechanisms: By altering the degree of shortening of the contractile ends of the muscle spindle, the sensitivity of the sensory part of the muscle spindle can be regulated.

This, in turn, stimulates the sensory neu-rons located at the center of the spindle.

For example, if the gamma motor neurons are stimulated before the muscle is lengthened, the middle of the muscle spin-dle is stretched even before the muscle actually lengthens. Thus, the muscle spindlesfunction as stretch receptors that inform other neu-rons in the brain and spinal cord of muscle length and the rate at which the muscle is stretching.īecause muscle spindles have their own motor supply, the degree of stretch of the muscle spindle can be altered by gamma motor neuron. This reflex (stretch reflex) also helps alter the muscle tone according to changes in posture. Thus, re-flexively (a reflex is an automatic, involuntary motor response to sensory stimulation), the muscle con-tracts when stretched to prevent overstretching the muscle. The sensory nerves also synapse (communicate) with motor neu-rons that innervate the muscle in question. This helps the brain coordinate muscle contraction. Impulses are conveyed to the cerebellum as well. The impulses are con-veyed to the cerebral cortex, providing feedback with regard to muscle position. In addition to the motor nerves, the center of the muscle spindle is surrounded by special sensory nerves that generate impulses every time the length of the muscle spindle is altered. When the gamma motor neurons are stimu-lated, the proteins (actin and myosin) concentrated at the ends of the muscle spindle contract, stretching the middle of the muscle spindle. The gamma motor neurons supply these fibers in com-parison with the other regular muscle fibers ( extra-fusal fibers) that are supplied by alpha motor neu-rons. Because the cell bodies of both motor neurontypes lie in the central nervous system, the brain can control the contraction of intrafusal and extrafusal fibers. The intrafusal fibers have their own sensory and motor nerve supply. The specialized muscle fibers in the muscle spindle are known as intrafusal fibers. The actin and myosin in the intrafusal fibers are concentrated to-ward the ends of the capsule. Muscles of the arms and legs have the highest number, with the muscles of the hand and foot having an abundance. The number of muscle spindles in each muscle is variable. On average, the length of the muscle spindle varies be-tween 2–4 mm (0.08–0.16 in).
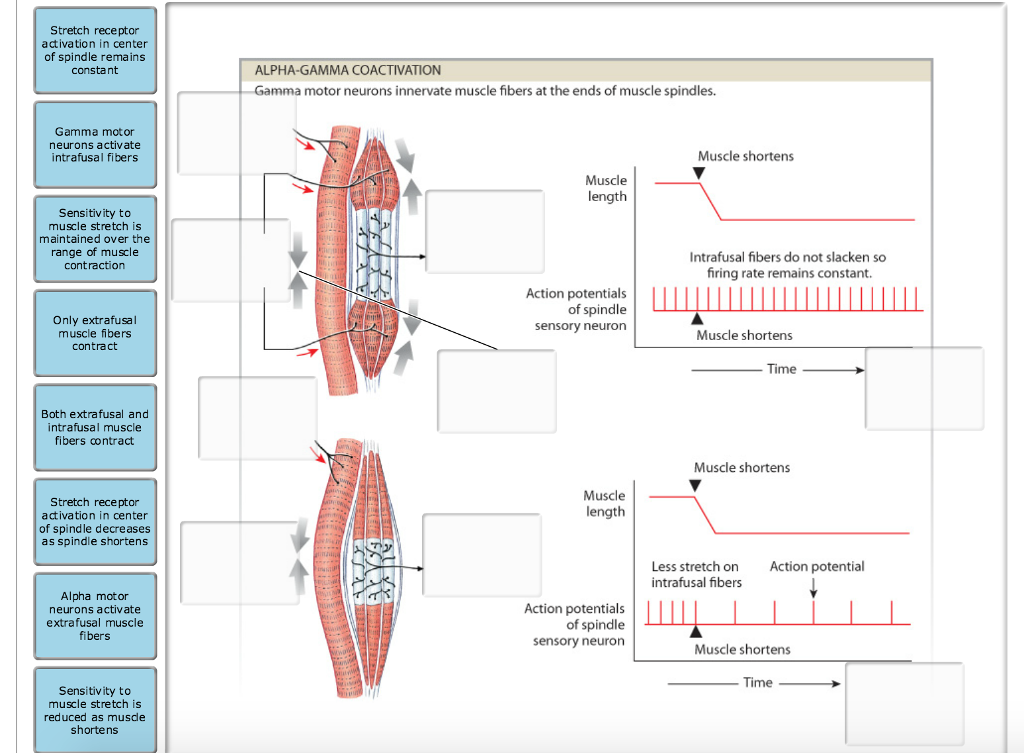
The muscle spindles are located parallel to other muscle fibers, and their length is al-tered as the whole muscle stretches or contracts. The ends of the muscle spindle capsule are attached to endomysium and perimysium. Muscle spindles are modified muscle fibers: 3–10 fibers that are surrounded by a capsule, giving it a spindle shape (see Figure 4.12). Muscle tone is maintained by stimulation of special-ized tissue ( muscle spindles) scattered within the muscle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
